Home / Handy Tips /

Shopping around for a new internet plan? Finding the perfect contract for your unique circumstances isn’t always easy, especially if you’re not familiar with the confusing terminology used to describe the different broadband networks.
In this article, we’ll explain the three main types of broadband found in Australia in a simple, easy-to-understand way. No geek speak – we promise! With this knowledge, you’ll be able to make an educated decision, and enjoy years of fast, reliable internet.
The three types of broadband we are going to look at are ADSL, cable, and fibre. Let’s get right into it.
What is ADSL broadband?

Traditional copper cables
ADSL – Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line – is a technology that enables existing copper phone lines to carry faster upload and download speeds.
Remember when you couldn’t talk on the phone and browse the web at the same time? Well, ADSL was developed in part to fix this issue. A device called a DSL filter separates digital data from landline calls, so the two can use the same line at once with little – usually no – interference.
ADSL is also a lot faster than old school dial-up. That being said, it’s a fair bit slower than other contemporary broadband technologies. Today’s ADSL2+ generates upload speeds of about 3.3Mbps, and a maximum download speeds of about 24Mbps.
One of the key benefits of ADSL2+ is the price and availability. Big telco companies already own kilometres and kilometres of copper wiring that runs all over the country, which can quickly and cheaply be converted into ADSL lines.
What is cable broadband?
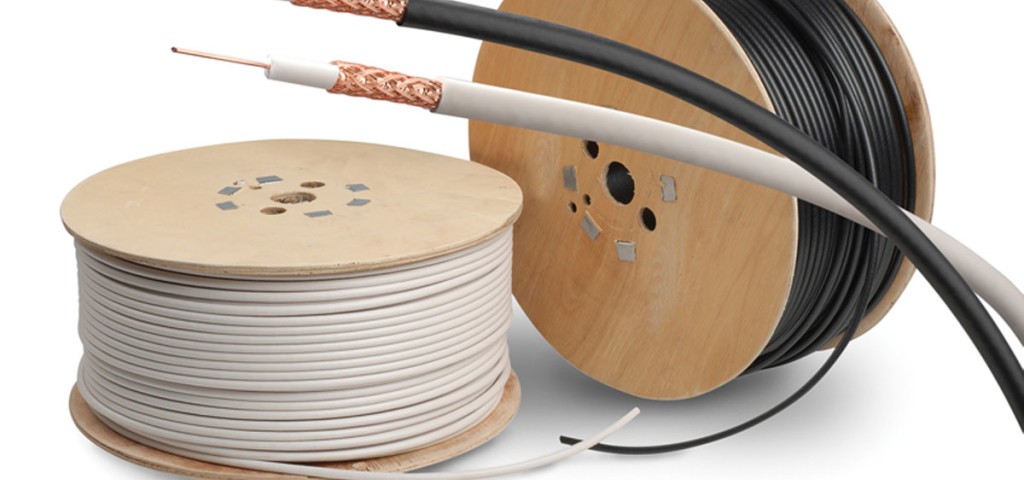

Coaxial cables. Photo by Emco Wires
Cable broadband – also referred to as hybrid fibre-coaxial (HFC) – is a network that combines fibre optic cables (which we will look at below) with slower coaxial cable.
Like traditional phone lines, coaxial cables are made from copper. However, with two layers separated by insulation, these cables are used exclusively to carry high volumes of data via radio signals (internet and cable TV) – not phone calls.
The best way to grasp cable broadband is to imagine the network like a tree. The trunk – in this case, the fibre optic lines – connects cities, towns, local fibre optic nodes, and major institutions (like universities). The branches – in this case, the coaxial cables – connect the trunk to individual homes.
Because cable broadband was designed for large data volumes, it offers much faster speeds. Some homes and institutions will experience speeds up to 100Mbps, though you can more realistically expect less than 50Mbps.
There are two major drawbacks of cable broadband. First, it’s availability. Cable broadband isn’t available at every address, and is only offered by Telstra and Optus. Second, it’s pricey – much more so than ADSL2+.
What is fibre broadband?
Fibre optic cables. Photo by iinet
Fibre broadband – also known as fibre-optic broadband and optical fibre broadband – is currently the fastest broadband technology on the market. Fibre broadband is being rolled out by the Australian government in a scheme called the National Broadband Network (NBN). The NBN aims to connect every home directly to fibre optic cables.
The NBN has garnered its fair share of negative press. If you’d like a little clarification as to what you can actually expect from the roll-out, check out our article Switching to the NBN: What to Consider and What to Expect.
Unlike phone lines and coaxial cables, optical fibres are made of thin glass through which light signals are transmitted. Optical fibres require very little maintenance, and are not subject electromagnetic interferences, so can deliver very high-speed, reliable internet connections.
The main benefit of fibre broadband is the speed. If your household consumes a lot of data – streaming videos, working from home, playing internet-connected video games, etc. – fibre broadband could be the best option.
There are, however, a few downsides:
- The speeds are not always faster than your current ADSL2+ or cable connection.
- Fibre broadband is not yet available in all households.
- Fibre broadband is expensive. Most telcos offer slower speeds at a cheaper rate. But if it’s speed you’re after, you’ll need to pay top dollar.
Want help with your internet?
The team at Computer Cures can take the guesswork out of choosing a broadband plan, and will liaise with ISPs to ensure you get the best deal possible. We can help with home network setup and installation, and can formulate a wifi setup that delivers strong and reliable signal to all areas of your home or office. We can also help with everything from your computer setup to your home theatre setup needs. Give us a call today on 1300 553 166, or fill out the form on this page, and we’ll get back to you ASAP.








Leave A Comment